Professor, Speech & Hearing Sciences
Co-Director, UW Institute for Learning & Brain Sciences
Director, NSF Science of Learning Center (LIFE)
Endowed Chair, Bezos Family Foundation Endowed Chair for Early Childhood Learning

Dr. Patricia K. Kuhl holds the Bezos Family Foundation Endowed Chair in Early Childhood Learning, Co-Director of the UW Institute for Learning and Brain Sciences, and Professor of Speech and Hearing Sciences at the University of Washington in Seattle. She is internationally recognized for her research on early language learning and bilingual brain development, for pioneering brain measures on young children, and for studies that show how young children learn. She presented her work at two White House conferences (Clinton White House in 1997 and Bush White House in 2001). Dr. Kuhl is a member of the National Academy of Sciences, the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, the Rodin Academy, and the Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters. She is a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, the Acoustical Society of America, the American Psychological Society, and the Cognitive Science Society. Dr. Kuhl was awarded the Silver Medal of the Acoustical Society of America in 1997. She received the University of Washington’s Faculty Lectureship Award in 1998. In 2005, she was awarded the Kenneth Craik Research Award from Cambridge University, and in 2007, the University of Minnesota’s Outstanding Achievement Award. In Paris in 2008, Dr. Kuhl was awarded the Gold Medal of the Acoustical Society of America for her work on early learning and brain development. In 2011, Dr. Kuhl received the IPSEN Foundation’s Jean-Louis Signoret Neuropsychology Prize, and in 2013 the William James Lifetime Achievement award. In 2014, Dr. Kuhl was awarded an Honorary Doctorate from Stockholm University, and in 2015 the George A. Miller Prize in Cognitive Neuroscience. Dr. Kuhl received the American Psychological Association’s Distinguished Scientific Contributions Award in 2018, and received an Honorary Doctorate from the Erikson Institute in 2020. Dr. Kuhl is co-author of The Scientist in the Crib: Minds, Brains, and How Children Learn (Harper Collins). Dr. Kuhl’s TED talk can be viewed at: http://www.ted.com/talks/patricia_kuhl_the_linguistic_genius_of_babies.html
EDUCATIONAL BACKGROUND
St. Cloud State University, B.A. (Speech Science; Psychology, 1964–1967)
University of Minnesota, M.A. (Speech Science, 1968–1971)
University of Minnesota, Ph.D. (Speech Science; Psychology, 1971–1973)
EMPLOYMENT RECORD
Washington University Central Institute for the Deaf Post-doctoral Fellow, 1973–76
University of Washington
Assistant Professor, 1977–1979
Associate Professor, 1979–1982
Professor (Speech and Hearing), 1982–present
Adjunct Professor (Psychology), 1985–present
Adjunct Professor (Otolaryngology), 1987–present
Adjunct Professor (Neuroscience), 1994–present
Adjunct Professor (Linguistics), 199–8present
Adjunct Professor (Education), 2004–present
MAJOR PROFESSIONAL OFFICES AND SERVICE
Executive Council: Acoustical Society of America, 1982–1986
Associate Editor: Journal of the Acoustical Society of America (1988–1992), Journal of Neuroscience (1989–1995), Developmental Science (2000–2012)
Member, University of Washington College of Arts and Science Council: 1982–1986
Member, Speech Communication Technical Committee: Acoustical Society, 1989–1992
Chair, Medals and Awards Committee: Acoustical Society of America, 1993–1995
Human Frontiers Scientific Review Committee: 1994–1999
Department Chair, Speech and Hearing Sciences, University of Washington: 1995–1999
Neuroscience Affiliate: G. Edelman’s Neuroscience Research Group, La Jolla, CA, 1994–2000
Board of Directors: American Institute of Physics, 1994–1996
Board of Directors (Governor Appointed): Washington Technology Center, 1994–1997
White House Speaker, President and Mrs. Clinton’s Summit on Early Learning: 1997
Co-Chair ASA/ICA: Joint International Meeting of the ASS and ICA, 1998
Board of Trustees: Neurosciences Research Foundation, Inc., 1994–1999
Vice-President Elect: Acoustical Society of America, 1995–1996
Vice President: Acoustical Society of America, 1996–1997
President-Elect: Acoustical Society of America, 1998–1999
President: Acoustical Society of America, 1999–2000
White House Speaker: First Lady Laura Bush’s Summit on Learning to Read: 2001
Co-Director Sante Fe Research Consortium: 2003–2005
Co-Chair (with Leo Beranik) ASA 75th Anniversary Celebration: 2004
Co-Director, University of Washington Institute for Learning & Brain Sciences: 2004–present
Member, ASA Publication Policy Committee: 2004–2005
Member, ASA Investment Committee: Acoustical Society of America, 2004–2006
Co-Director, NSF Science of Learning Center (LIFE Center): 2004–2005
International Advisory Board: Nippon Telegraph and Telephone, 2004–2008
American Association for the Advancement of Science: Section Z, Linguistics, 2005
Director, NSF Science of Learning Center (LIFE Center): 2005–2018
Chair, AAAS Nominating Committee: Section J, Psychology, 2006
Member, National Academy of Science Troland Award Committee: 2011–2012
Chair, National Academy of Science Troland Award Committee: 2012–2013
NAS Chair of Membership (Section 52 Psychological & Cognitive Sciences): 2014–2016
White House Speaker, President Obama’s Summit on Early Learning: 2014
NSF Alan T Waterman Award Committee: 2015–2017
Bezos Family Foundation Scientific Advisory Board: 2015–present
AAAS Psychology (Section J) Steering Committee: 2016–2019
NAS Chair of Section 52 (Psychological & Cognitive Sciences): 2016–2019
National Academy of Science Council: 2019–2022
Global Science of Learning (GSOLEN): Advisory Group: 2019-
PUBLICATIONS
Mittag, M., Larson, E., Clarke, M., Taulu, S., & Kuhl, P. K. (2021). Auditory deficits in infants at risk for dyslexia during a linguistic sensitive period predict future language. NeuroImage, 30, 102578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2021.102578
Kuhl, P. K. (2021, in press). Language. In E. R. Kandel, J. D. Koester, S. H. Mack, & S. A. Siegelbaum (Eds.), Principles of neural science (6th ed.). McGraw Hill.
Kuhl, P. K. (2021, in press). Infant speech perception: Integration of multimodal data leads to a new hypothesis—Sensorimotor mechanisms underlie learning. In Minnesota Symposia on Child Psychology (Vol. 40, pp. 113–158). Wiley.
Ferjan Ramírez, N., Hippe, D. S., & Kuhl, P. K. (2021). Comparing automatic and manual measures of parent-infant conversational turns: A word of caution. Child Development. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.13495
Corrigan, N. M., Varnykh, V. L., Hippe, D. S., Owen, J. P., Huber, E., Zhoa, T. C., & Kuhl, P. K. (2021). Myelin development in cerebral gray and white matter during adolescence and late childhood. NeuroImage, 277, 117678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117678
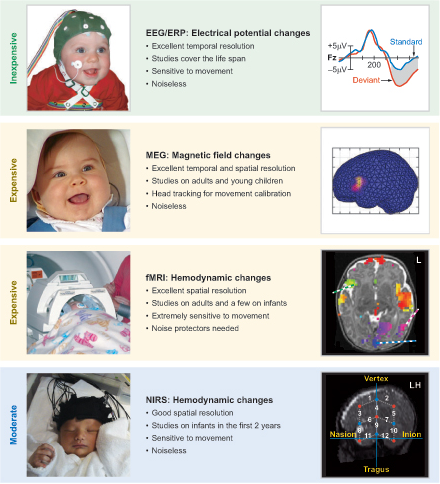
Bosseler, A. N., Clarke, M., Tavabi, K., Larson, E. D., Hippe, D. S., Taulu, S., & Kuhl, P. K. (2021). Using magnetoencephalography to examine word recognition, lateralization, and future language skills in 14-month-old infants. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 47, 100901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2020.100901
Sundara, M., Wards, N., Conboy, B., & Kuhl, P. K. (2020, in press). Exposure to a second language in infancy alters speech production. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition.
Mamiya, P. C., Richards, T., Corrigan, N. M., & Kuhl, P. K. (2020). Strength of ventral tegmental area connections with left caudate nucleus is related to conflict monitoring. Frontiers in Psychology. On-line access prior to publication, doi.org/10.33.89/fpsyg.2019.02869
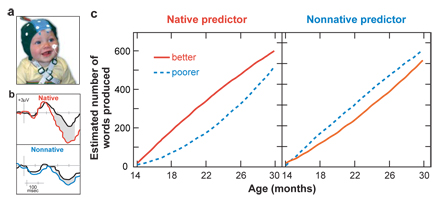
Ferjan Ramírez, N., Lytle, S., & Kuhl, P. K. (2020, in press). Parent coaching increases conversational turns and advances infant language development. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Ferjan Ramírez, N., & Kuhl, P. K. (2020). Early second language learning through SparkLing™: Scaling up a language intervention in infant education centers. Mind, Brain, and Education. On-line access prior to publication, doi.org/10.1111/mbe.12232
Zhao, M., Masapollo, M., Polka, L., Menard, L. & Kuhl, P. K. (2019). Effects of formant proximity and stimulus prototypicality on the neural discrimination of vowels: Evidence from the auditory Frequency-Following Response. Brain and Language, 194, 77–83.
Lin, J.-F. L., Imada, T., & Kuhl, P. K. (2019). Neuroplasticity, bilingualism, and mental mathematics: A behavior-MEG study. Brain and Cognition, 134, 122–134.
Kuhl, P. K., Lim, S.-S., Guerriero, S. & Van Damme, D. (2019). Developing Minds in the Digital Age: Towards a Science of Learning for 21st Century Education. Paris, France: OECD Publishing.
Kuhl, P. K., & Ferjan Ramírez, N. (2019). Neuroscience and education: How early brain development affects school. In P. K. Kuhl, S.-S. Lim, S. Guerriero & D. Van Damme (Eds.), Developing Minds in the Digital Age: Towards a Science of Learning for 21st Century Education. Paris, France: OECD Publishing.
Zhao, T. C., & Kuhl, P. K. (2018). Linguistic effect on speech perception observed at the brainstem. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 115, 8716–8721.
Mamiya, P. C., Richards, T. L., & Kuhl, P. K. (2018). Right forceps minor and anterior thalamic radiation predict executive function skills in young bilingual adults. Frontiers in Psychology-Language Sciences, 9, 1–10.
Lytle, S. R., & Kuhl, P. K. (2018). Social interaction and language acquisition: Toward a neurobiological view. In E. M. Fernández & H. S. Cairns (Eds.), Blackwell Handbooks in Linguistics. The Handbook of Psycholinguistics (pp. 615–634). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Blackwell.
Lytle, S. R., García-Sierra, A., & Kuhl, P. K. (2018). Two are better than one: Infant language learning from video improves in the presence of peers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115, 9859–9866.
Lin, J.-F. L., Imada., Kuhl, P. K., & Lin, F.-H. (2018). Incongruent pitch cues are associated with increased activation and functional connectivity in the frontal areas. Scientific Reports, 8, 5206. DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-23287-5
Ferjan Ramírez, N., & Kuhl, P. K. (2017). Bilingual baby: Foreign language intervention in Madrid’s Infant Education Centers. Mind, Brain, and Education, 11, 133–143.
Ferjan Ramírez, N., Ramírez, R. R., Clarke, M., Taulu, S., & Kuhl, P. K. (2017). Speech discrimination in 11-month-old bilingual and monolingual infants: A magnetoencephalography study. Developmental Science, 20: e12427.
Fish, M. S., García-Sierra, A., Ramírez-Esparza, N., & Kuhl, P. K. (2017). Infant-directed speech in English and Spanish: Assessments of monolingual and bilingual caregiver VOT. Journal of Phonetics, 63, 19–34.
Kuhl, P. K. (2017). Big surprises from little brains. Early Childhood Matters, 126, 20–25.
Lytle, S. R., & Kuhl, P. K. (2017). Social interaction and language acquisition: Toward a neurobiological view. In E. M. Fernández & H. S. Cairns (Eds.), The Handbook of Psycholinguistics, 1st Edition (pp. 615–634). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Ramírez-Esparza N., García-Sierra, A., & Kuhl, P. K. (2017). Look whos’ talking NOW! Parentese speech, social context, and language development across time. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 1–27.
Ramírez-Esparza, N., García-Sierra, A., & Kuhl, P. K. (2017). The impact of early social interactions on later language development in Spanish-English bilingual infants. Child Development,88, 1216–1234.
Zhao, T. C., & Kuhl, P. K. (2017). Effects of enriched auditory experiences on infants' speech perception during the first year of life. PROSPECTS, 46, 235–247.
Zhao, T. C., Lam, H. T. G., Sohi, H., & Kuhl, P. K. (2017). Neural processing of musical meter in musicians and non-musicians. Neuropsychologia, 106, 289–297.
García-Sierra, A., Ramírez-Esparza, N., & Kuhl, P. K. (2016). Relationships between quantity of language input and brain responses in bilingual and monolingual infants. International Journal of Psychophysics, 110, 1–17.
Kuhl, P. K. (2016). Language and the social brain: The power of surprise in science. In R. J. Sternberg, S. T. Fiske, & D. J. Foss (Eds.), Scientists Making a Difference (pp. 206-209). New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Kuhl, P. K., Stevenson, J., Corrigan, N. M., van den Bosch, J. F. F., Deniz Can, D., & Richards, T. (2016). Neuroimaging of the bilingual brain: Structural brain correlates of listening and speaking in a second language. Brain & Language, 162, 1–9.
Mamiya, P. C., Richards, T. L., Coe, B. P., Eichler, E. E., & Kuhl, P. K. (2016). Brain white matter structure and COMT gene are linked to second-language learning in adults. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113, 7249–7254.
Meltzoff, A. N., & Kuhl, P. K. (2016). Exploring the infant social brain: What's going on in there? Zero to Three, 36, 2-9.
Nakagawa, J., Imada, T., Hosoi, H., Meltzoff, A. N., & Kuhl, P. K. (2016). Development of an infant-friendly flat-panel earphone for non-invasive functional brain imaging on awake babies using cartilage conduction. Transactions of Japanese Society for Medical and Biological Engineering, 54, 1–2.
Zhao, T. C., & Kuhl, P. K. (2016). Musical intervention enhances infants’ neural processing of temporal structure in music and speech. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113, 5212–5217.
Conboy, B. T., Brooks, R., Meltzoff, A. N., & Kuhl, P. K. (2015). Social interaction in infants’ learning of second-language phonetics: An exploration of brain-behavior relations. Developmental Neuropsychology, 40, 216–229.
Kuhl, P. K. (2015). Baby talk. Scientific American, 313, 64–69.
Moon, C., Zernzach, R. C., & Kuhl, P. K. (2015). Mothers say “baby” and their newborns do not choose to listen: A behavioral preference study to compare with ERP results. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 9, 153.
Zhao, T. C., & Kuhl, P. K. (2015). Effect of musical experience on learning lexical tone categories. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 137, 1452–1463.
Zhao, T. C., & Kuhl, P. K. (2015). Higher-level linguistic categories dominate over lower-level acoustics in lexical tone processing. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 138, 133–137.
Kuhl, P. K. (2014). Early language learning and the social brain. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology, 79, 211-220.
Kuhl, P. K., Ramírez, R. R., Bosseler, A., Lin, J.-F. & Imada, T. (2014). Infants’ brain responses to speech suggest Analysis by Synthesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 111, 11238–11245.
Ramírez-Esparza, N., García-Sierra, A., & Kuhl, P. K. (2014). Look who’s talking: Speech style and social context in language input are linked to concurrent and future speech development. Developmental Science, 17, 880–891.
Akiyama, L. F., Richards, T. R., Imada, T., Dager, S. R., Wroblewski, L., & Kuhl, P. K. (2013). Age-specific average head template for typically developing 6-month-old infants. PLoS ONE, 8, 1–9.
Bosseler, A. N., Taulu, S., Pihko, E., Mäkelä, J. P., Imada, T., Ahonen, A., & Kuhl, P. K. (2013). Theta rhythms index perceptual narrowing in infant speech perception. Frontiers in Psychology, 4, 1–12.
Deniz Can, D., Richards, T., & Kuhl, P. K. (2013). Early gray-matter and white-matter concentration in infancy predict later language skills: A whole-brain voxel-based morphometry study. Brain & Language, 124, 34–44.
Kuhl, P. K., Coffey-Corina, S., Padden, D. M., Munson, J., Estes, A., & Dawson, G. (2013). Brain responses to words in 2-year-olds with Autism predict developmental outcomes at age 6. PLoS ONE, 8, 1–13.
Moon, C., Lagercrantz, H., & Kuhl, P. K. (2013). Language experienced in utero affects vowel perception after birth: A two country study, Acta Pediatrica, 102, 156–160.
Kuhl, P. K., & Damasio, A. (2012). Language, in E. R. Kandel., J. H. Schwartz, T. M. Jessell, S. Siegelbaum, & J. Hudspeth (Eds.), Principles of neural science: 5th Edition (pp. 1353–1372). New York, NY: McGraw Hill.
Lin, J.-F. L., Imada, T., & Kuhl, P. K. (2012). Mental addition in bilinguals: An fMRI study of task-related and performance-related activation. Cerebral Cortex, 22, 1851–1861.
Ramírez-Esparza, N., Harris, K., Hellermann, J., Richard, C., Kuhl, P. K., & Reder, S. (2012). Socio-interactive practices and personality in adult learners of English with little formal education. Language Learning, 62, 541–570.
Rivera-Gaxiola. M., García-Sierra, A., Lara-Ayala, L., Cadena, C., Jackson-Maldonado, D., & Kuhl, P. K. (2012). Event-related potentials to an English/Spanish syllabic contrast in Mexican 10–13 month-old infants. ISRN Neurology, 2012, 1‐9.
Conboy, B. T., & Kuhl, P. K. (2011). Impact of second-language experience in infancy: Brain measures of first- and second-language speech perception. Developmental Science, 14, 242–248.
García-Sierra, A., Rivera-Gaxiola, M., Percaccio, C. R., Conboy, B. T., Romo, H., Klarman, L., Ortiz, S., & Kuhl, P. K. (2011). Bilingual language learning: An ERP study relating early brain responses to speech, language, and later word production. Journal of Phonetics, 39, 546–557.
Kuhl, P. K. (2011). Brain mechanisms underlying the critical period for language: Linking theory and practice, in A. M. Battro, S. Dehaene, & W. J. Singer (Eds.), Human neuroplasticity and education (pp. 33–59). The Pontifical Academy of Sciences: Vatican City.
Kuhl, P. K. (2011). Early language learning and literacy: Neuroscience implications for education. Mind, Brain, and Education, 5, 128–142.
Kuhl, P. K. (2011). Social mechanisms in early language acquisition: Understanding integrated brain systems supporting language. In J. Decety & J. Cacioppo (Eds.) The Oxford handbook of social neuroscience (pp. 649–667). Oxford United Kingdom: Oxford University Press.
Kuhl, P. K. (2011). Who's Talking? Science, 29, 529–530.
Sundara, M., Demuth, K., & Kuhl, P. K. (2011). Sentence-position effects on children’s perception and production of English 3rd person singular –s. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 54, 55–71.
Zhao, T., Moon, C., Lagercrantz, H., & Kuhl, P. K. (2011). Prenatal motherese? Newborn speech perception is enhanced by having a younger sibling. Psi Chi, The International Honor Society in Psychology, 16, 90–94.
Kuhl, P. K. (2010). Brain mechanisms in early language acquisition. Neuron, 67, 713–722.
Lebedeva, G. C., & Kuhl, P. K. (2010). Sing that tune: Infants' perception of melody and lyrics and the facilitation of phonetic recognition in songs. Infant Behavior and Development, 33, 419–430.
Raizada, R. D. S., Tsao, F.-M., Liu, H.-M., Holloway, I. D., Ansari, D., & Kuhl, P. K. (2010). Linking brain-wide multivoxel activation patterns to behaviour: Examples from language and math. NeuroImage, 51, 462–471.
Raizada, R. D. S., Tsao, F.-M., Liu, H.-M., & Kuhl, P. K. (2010). Quantifying the adequacy of neural representations for a cross-language phonetic discrimination task: Prediction of individual differences. Cerebral Cortex, 20, 1–12.
Kuhl, P. K. (2009). Early language acquisition: Neural substrates and theoretical models. In M. S. Gazzaniga (Ed.), The Cognitive Neurosciences, 4th Edition (pp. 837–854). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Kuhl, P. K. (2009). Early language acquisition: Phonetic and word learning, neural substrates, and a theoretical model. In B. Moore, L. Tyler, & W. Marslen-Wilson (Eds.), The Perception of Speech: From Sound to Meaning (pp. 103–131). Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press.
Liu, H.-M., Tsao, F.-M., & Kuhl, P. K. (2009). Age-related changes in acoustic modifications of Mandarin maternal speech to preverbal infants and five-year-old children: A longitudinal study. Journal of Child Language, 36, 909–922.
Meltzoff, A. N., Kuhl, P. K., Movellan, J., & Sejnowski, T. J. (2009). Foundations for a new science of learning. Science, 325, 284–288.
Wang, Y., Kuhl, P. K., Chen, C., & Dong, Q. (2009). Sustained and transient language control in the bilingual brain. NeuroImage, 47, 414–422.
Zhang, Y., Kuhl, P. K., Imada, T., Iverson, P., Pruitt, J., Stevens, E. B., Kawakatsu, M., Tohkura, Y., & Nemoto, I. (2009). Neural signatures of phonetic learning in adulthood: A magnetoencephalography study. Neuroimage, 46, 226–240.
Conboy, B. T., Rivera-Gaxiola, M., Silva-Pereyra, J., & Kuhl, P. K. (2008). Event-related potential studies of early language processing at the phoneme, word, and sentence levels. In A. D. Friederici & G. Thierry (Eds.), Trends in Language Acquisition Research, 5, 23–64. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: John Benjamins.
Conboy, B.T., Sommerville, J. A., & Kuhl, P. K. (2008). Cognitive control factors in speech
perception at 11 months. Developmental Psychology, 44, 1505–1512.
Doupe, A. J., & Kuhl, P. K. (2008). Birdsong and human speech: Common themes and mechanisms. In H. P. Zeigler, & P. Marler (Eds.), Neuroscience of Birdsong (pp. 5–31). New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Kuhl, P. K. (2008). Linking infant speech perception to language acquisition: Phonetic learning predicts language growth. In J. Colombo, P. McCardle, & L. Freund (Eds.), Infant pathways to language: Methods, models, and research directions (pp. 213–243). New York, NY: Erlbaum.
Kuhl, P. K., Conboy, B. T., Coffey-Corina, S., Padden, D., Rivera-Gaxiola, M., & Nelson, T. (2008). Phonetic learning as a pathway to language: New data and Native Language Magnet Theory, expanded (NLM-e). Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 363, 979–1000.
Kuhl, P. K., & Rivera-Gaxiola, M. (2008). Neural substrates of language acquisition. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 31, 511–534.
Lin, J.-F., Imada, T., Tanaka, K., Hirai, K., Maeshima, K., Nemoto, I., & Kuhl, P. K. (2008). The effect of translation on bilingual mental addition revealed by magnetoencephalography (MEG). In R. Kakigi, K. Yokosawa, & S. Kuriki. (Eds.), Biomagnetism: Interdisciplinary Research and Exploration (pp. 212–214). Sapporo, Japan: Hokkaido University Press.
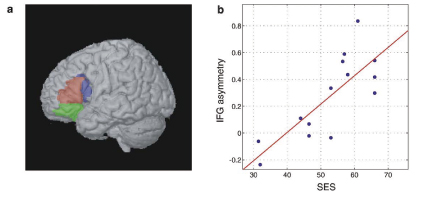
Raizada, R. D. S., Richards, T. L., Meltzoff, A. N., & Kuhl, P. K. (2008). Socioeconomic status predicts hemispheric specialization of the left inferior frontal gyrus in young children. NeuroImage, 40, 1392–1401.
Conboy, B. T., & Kuhl, P. K. (2007). Early speech perception: Developing a culturally specific way of listening through social interaction. In S. Bråten (Ed.), On Being Moved: From Mirror Neurons to Empathy (pp. 175–199). Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press.
Kuhl, P. K. (2007). Is speech learning ‘gated’ by the social brain? Developmental Science, 10, 110–120.
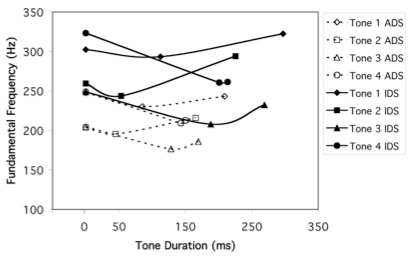
Liu, H.-M., Tsao, F.-M., & Kuhl, P. K. (2007). Acoustic analysis of lexical tone in Mandarin infant-directed speech. Developmental Psychology, 43, 912–917.
Rivera-Gaxiola, M., Silva-Pereyra, J., Klarman, L., García-Sierra, A., Lara-Ayala, L., Cadena-Salazar, C., & Kuhl, P. K. (2007). Principal component analyses and scalp distribution of the auditory P150–250 and N250–550 to speech contrasts in Mexican and American infants. Developmental Neuropsychology, 31, 363–378.
Silva-Pereyra, J., Conboy, B. T., Klarman, L., & Kuhl, P. K. (2007). Grammatical processing without semantics? An event-related brain potential study of preschoolers using jabberwocky sentences. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 19, 1–16.
Wang, Y., Lin, L., Kuhl, P., & Hirsch, J. (2007). Mathematical and linguistic processing differs between native and second languages: An fMRI study. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 1, 68–82.
Bransford, J., Barron, B., Pea, R., Meltzoff, A., Kuhl, P., Bell, P., Stevens, R., Schwartz, D., Vye, N., Reeves, B., Roschelle, J., & Sabelli, N. (2006). Foundations and opportunities for an interdisciplinary science of learning. In K. Sawyer (Ed.), The Cambridge Handbook of the Learning Sciences (pp. 19–34). New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Bransford, J., Vye, N., Stevens, R., Kuhl, P., Schwartz, D., Bell, P., Meltzoff, A., Barron, B., Pea, R., Reeves, B., Roschelle, J., & Sabelli, N. (2006). Learning theories and education: Toward a decade of synergy. In P. Alexander & P. Winne (Eds.), Handbook of Educational Psychology, 2nd edition (pp. 209–244). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
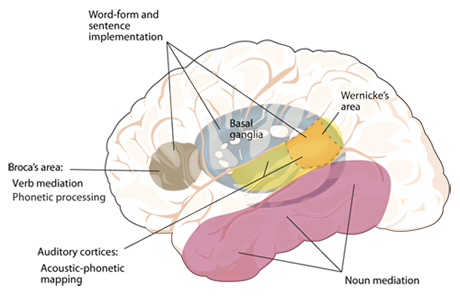
Imada, T., Zhang, Y., Cheour, M., Taulu, S., Ahonen, A., & Kuhl, P. K. (2006). Infant speech perception activates Broca’s Area: A developmental magnetoencephalography study. NeuroReport, 17, 957–962.
Kuhl, P. K., Stevens, E., Hayashi, A., Deguchi, T., Kiritani, S., & Iverson, P. (2006). Infants show a facilitation effect for native language phonetic perception between 6 and 12 months. Developmental Science, 9, F13–F21.
Tsao, F.-M., Liu, H.-M., & Kuhl, P. K. (2006). Perception of native and non-native affricate-fricative contrasts: Cross-language tests on adults and infants. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 120, 2285–2294.
Conboy, B. T., Rivera-Gaxiola, M., Klarman, L., Aksoylu, E., & Kuhl, P. K. (2005). Associations between native and nonnative speech sound discrimination and language development at the end of the first year. Proceedings Supplement of the 29th Annual Boston University Conference on Language Development.
Kuhl, P. K., Coffey-Corina, S., Padden, D., & Dawson, G. (2005). Links between social and linguistic processing of speech in preschool children with autism: Behavioral and electrophysiological measures. Developmental Science, 8, F9–F20.
Kuhl, P. K., Conboy, B. T., Padden, D., Nelson, T., & Pruitt, J. (2005). Early speech perception and later language development: Implications for the "critical period". Language Learning and Development, 1, 237–264.
Liu, H.-M., Tsao, F.-M., & Kuhl, P. K. (2005). The effect of reduced vowel working space on speech intelligibility in Mandarin-speaking young adults with cerebral palsy. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 117, 3879–3889.
Rivera-Gaxiola, M., Klarman, L., García-Sierra, A., & Kuhl, P. K. (2005). Neural patterns to speech and vocabulary growth in American infants. NeuroReport, 16, 495–498.
Rivera-Gaxiola, M., Silva-Pereyra, J., & Kuhl, P. K. (2005). Brain potentials to native and non-native speech contrasts in 7- and 11-month-old American infants. Developmental Science, 8, 162–172.
Silva-Pereyra, J. F., Klarman, L., Lin, L. J.-F., & Kuhl, P. K. (2005). Sentence processing in 30-month-old children: An event related potential study. NeuroReport, 16, 645–648.
Silva-Pereyra, J., Rivera-Gaxiola, M., & Kuhl, P. K. (2005). An event-related brain potential study of sentence comprehension in preschoolers: Semantic and morphosyntactic processing. Cognitive Brain Research, 23, 247–258.
Zhang, Y., Kuhl, P. K., Imada, T., Kotani, M., & Tohkura, Y. (2005). Effects of language experience: Neural commitment to language-specific auditory patterns. NeuroImage, 26, 703–720.
Cheour, M., Imada, T., Taulu, S., Ahonen, A., Salonen, J., & Kuhl, P. K. (2004). Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is feasible for infant assessment of auditory discrimination. Experimental Neurology, 190, 44–51.
Kuhl, P. K. (2004). Early language acquisition: Cracking the speech code. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 5, 831–843.
Tsao, F.-M., Liu, H.-M., & Kuhl, P. K. (2004). Speech perception in infancy predicts language development in the second year of life: A longitudinal study. Child Development, 75, 1067–1084.
de Boer, B., & Kuhl, P. K. (2003). Investigating the role of infant-directed speech with a computer model. Acoustic Research Letters Online (ARLO), 4, 129–134.
Iverson, P., Kuhl, P. K., Akahane-Yamada, R., Diesch, E., Tohkura, Y., Kettermann, A., & Siebert, C. (2003). A perceptual interference account of acquisition difficulties for non-native phonemes. Cognition, 87, B47–B57.
Kuhl, P. K. (2003). Human speech and birdsong: Communication and the social brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 100, 9645–9646.
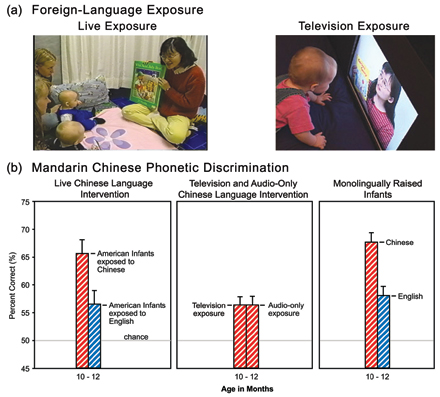
Kuhl, P. K., Tsao, F.-M., & Liu, H.-M. (2003). Foreign-language experience in infancy: Effects of short-term exposure and social interaction on phonetic learning. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 100, 9096–9101.
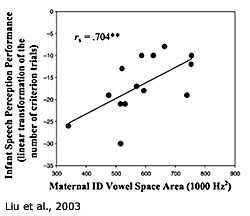
Liu, H.-M, Kuhl, P. K., & Tsao, F.-M. (2003). An association between mothers' speech clarity and infants’ speech discrimination skills. Developmental Science, 6, F1–F10.
Wang, Y., & Kuhl, P. K. (2003). Evaluating the “critical period” hypothesis: Perceptual learning of Mandarin tones in American adults and American children at 6, 10, and 14 years of age. Proceedings of the 15th International Congress of Phonetic Sciences, 1537–1540.
Kuhl, P. K. (2001). Speech, language, and developmental change. In F. Lacerda, C. von Hofsten, & M. Heimann (Eds.), Emerging Cognitive Abilities in Early Infancy (pp. 111–133). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Kuhl, P. K., Tsao, F.-M., Liu, H.-M., Zhang, Y., & de Boer, B. (2001). Language/culture/mind/brain: Progress at the margins between disciplines. In A. R. Domasio et al. (Eds.), Unity of Knowledge: The Convergence of Natural and Human Science (pp. 136–174). New York, NY: The New York Academy of Sciences.
Iverson, P., & Kuhl, P. K. (2000). Perceptual magnet and phoneme boundary effects in speech perception: Do they arise from a common mechanism? Perception and Psychophysics, 62, 874–886.
Kuhl, P. K. (2000). A new view of language acquisition. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 97, 11850–11857.
Kuhl, P. K. (2000). Language, mind, and brain: Experience alters perception. In M. S. Gazzaniga (Ed.), The New Cognitive Neurosciences (2nd ed.) (pp. 99–115). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Doupe, A. J., & Kuhl, P. K. (1999). Birdsong and speech: Common themes and mechanisms. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 22, 567–631.
Gopnik, A., Meltzoff, A. N., & Kuhl, P. K. (1999). The Scientist in the Crib: Minds, Brains, and How Children Learn. New York, NY: William Morrow.
Kuhl, P. K. (1999). Speech, language, and the brain: Innate preparation for learning. In M. D. Hauser & M. Konishi (Eds.), The Design of Animal Communication (pp. 419–450). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Kuhl, P. K. (1998). Effects of language experience on speech perception. In P. K. Kuhl & L. Crum (Eds.), Proceedings 16th International Congress on Acoustics and 135th Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America (Vol. 3, pp. 1601–1602). Woodbury, NY: Acoustical Society of America.
Kuhl, P. K. (1998). Language, culture, and intersubjectivity: The creation of shared perception. In S. Bråten (Ed.), Intersubjective Communication and Emotion in Early Ontogeny (pp. 297–315). Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press.
Kuhl, P. K. (1998). The development of language. In C. van Euler, I. Lundberg, & R. Llinás (Eds.), Basic Mechanisms in Cognition and Language (pp. 175–195). New York, NY: Elsevier.
Kuhl, P. K. (1998). The development of speech and language. In T. J. Carew, R. Menzel, & C. J. Shatz (Eds.), Mechanistic Relationships Between Development and Learning (pp. 53-73). New York, NY: Wiley.
Green, K. P., Tomiak, G. R., & Kuhl, P. K. (1997). The encoding of rate and talker information during phonetic perception. Perception and Psychophysics, 59, 675–692.
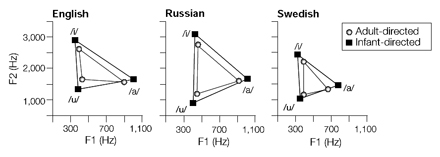
Kuhl, P. K., Andruski, J. E., Chistovich, I. A., Chistovich, L. A., Kozhevnikova, E. V., Ryskina, V. L., Stolyarova, E. I., Sundberg, U., & Lacerda, F. (1997). Cross-language analysis of phonetic units in language addressed to infants. Science, 277, 684–686.
Kuhl, P. K., & Meltzoff, A. N. (1997). Evolution, nativism, and learning in the development of language and speech. In M. Gopnik (Ed.), The Inheritance and Innateness of Grammars (pp. 7–44). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Andruski, J. E., & Kuhl, P. K. (1996). The acoustic structure of vowels in mothers’ speech to infants and adults. Proceedings of the 1996 International Conference on Spoken Language Processing, 3, 1545–1548.
Iverson, P., & Kuhl, P. K. (1996). Influences of phonetic identification and category goodness on American listeners' perception of /r/ and /l/. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 99, 1130–1140.
Kuhl, P. K., & Meltzoff, A. N. (1996). Infant vocalizations in response to speech: Vocal imitation and developmental change. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 100, 2425–2438.
Willerman, R., & Kuhl, P. K. (1996). Cross-language speech perception: Swedish, English, and Spanish speakers' perception of front rounded vowels. Proceedings of the 1996 International Conference on Spoken Language Processing, 1, 442–445.
Iverson, P., & Kuhl, P. K. (1995). Mapping the perceptual magnet effect for speech using signal detection theory and multidimensional scaling. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 97, 553–562.
Kuhl, P. K. (1995). Mechanisms of developmental change in speech and language. Proceedings of the XIIIth International Congress on Phonetic Sciences, 2, 132–139.
Kuhl, P. K. (1995). The acquisition of language and speech. In G. Bloothooft, V. Hazan, D. Huber, & J. Llisterri (Eds.), European Studies in Phonetics and Speech Communication (pp. 93–98). Utrecht, The Netherlands: OTS Publications.
Kuhl, P. K., & Iverson, P. (1995). Linguistic experience and the “perceptual magnet effect.” In W. Strange (Ed.), Speech Perception and Linguistic Experience: Issues in Cross-Language Research (pp. 121–154). Timonium, MD: York Press.
Kuhl, P. K., & Meltzoff, A. N. (1995). Vocal learning in infants: Development of perceptual-motor links for speech. Proceedings of the XIIIth International Congress on Phonetic Sciences, 1, 146–149.
Green, K. P., Stevens, E. B., & Kuhl, P. K. (1994). Talker continuity and the use of rate information during phonetic perception. Perception & Psychophysics, 55, 249–260.
Kuhl, P. K. (1994). Forming the brain's perceptual maps: Effects of language experience on speech perception. In Brain and Communication: 1994 Yakult International Symposium (pp. 1–22). Japan: Yakult Honsha Co.
Kuhl, P. K. (1994). Learning and representation in speech and language. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 4, 812–822.
Kuhl, P. K. (1994). Speech perception. In F. D. Minifie (Ed.), Introduction to Communication Sciences and Disorders (pp. 77–148). San Diego, CA: Singular.
Kuhl, P. K., Tsuzaki, M., Tohkura, Y., & Meltzoff, A. N. (1994). Human processing of auditory-visual information in speech perception: Potential for multimodal human-machine interfaces. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (pp. 539–542). Tokyo: Acoustical Society of Japan.
Meltzoff, A. N., & Kuhl, P. K. (1994). Faces and speech: Intermodal processing of biologically relevant signals in infants and adults. In D. J. Lewkowicz & R. Lickliter (Eds.), The Development of Intersensory Perception: Comparative Perspectives (pp. 335–369). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Goodsitt, J. V., Morgan, J. L., & Kuhl, P. K. (1993). Perceptual strategies in prelingual speech segmentation. Journal of Child Language, 20, 229–252.
Kuhl, P. K. (1993). Developmental speech perception: Implications for models of language impairment. In P. Tallal, A. M. Galaburda, R. R. Llinás & C. von Euler (Eds.), Temporal Information Processing in the Nervous System. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences (Vol. 682, pp. 248–263). New York, NY: The New York Academy of Sciences.
Kuhl, P. K. (1993). Early linguistic experience and phonetic perception: Implications for theories of developmental speech perception. Journal of Phonetics, 21, 125–139.
Kuhl, P. K. (1993). Infant speech perception: A window on psycholinguistic development. International Journal of Psycholinguistics, 9, 33–56.
Kuhl, P. K. (1993). Innate predispositions and the effects of experience: The native language magnet theory. In B. de Boysson-Bardies, S. de Schonen, P. Jusczyk, P. McNeilage, & J. Morton (Eds.), Developmental Neurocognition: Speech and Face Processing in the First Year of Life (pp. 259–274). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Davis, K., & Kuhl, P. K. (1992). Best exemplars of English velar stops: A first report. In J. J. Ohala, T. M. Nearey, B. L. Derwing, M. M. Hodge, & G. E. Wiebe (Eds.), Proceedings of the International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (pp. 495–498). Edmonton, AB: University of Alberta.
Kuhl, P. K. (1992). Infants’ perception and representation of speech: Development of a new theory. In J. J. Ohala, T. M. Nearey, B. L. Derwing, M. M. Hodge, & G. E. Wiebe (Eds.), Proceedings of the International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (pp. 449–456). Edmonton, AB: University of Alberta.
Kuhl, P. K. (1992). Psychoacoustics and speech perception: Internal standards, perceptual anchors, and prototypes. In L. A. Werner & E. W. Rubel (Eds.), Developmental Psychoacoustics (pp. 293–332). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Kuhl, P. K. (1992). Speech prototypes: Studies on the nature, function, ontogeny and phylogeny of the “centers” of speech categories. In Y. Tohkura, E. Vatikiotis-Bateson, & Y. Sagisaka (Eds.), Speech Perception, Production and Linguistic structure (pp. 239:264). Tokyo, Japan: Ohmsha.
Kuhl, P. K., Williams, K. A., Lacerda, F., Stevens, K. N., & Lindblom, B. (1992). Linguistic experience alters phonetic perception in infants by 6 months of age. Science, 255, 606–608.
Marean, G. C., Werner, L. A., & Kuhl, P. K. (1992). Vowel categorization by very young infants. Developmental Psychology, 28, 396–405.
Green, K. P., & Kuhl, P. K. (1991). Integral processing of visual place and auditory voicing information during phonetic perception. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 17, 278–288.
Green, K. P., Kuhl, P. K., Meltzoff, A. N., & Stevens, E. B. (1991). Integrating speech information across talkers, gender, and sensory modality: Female faces and male voices in the McGurk effect. Perception & Psychophysics, 50, 524–536.
Kuhl, P. K. (1991). Human adults and human infants show a "perceptual magnet effect" for the prototypes of speech categories, monkeys do not. Perception & Psychophysics, 50, 93–107.
Kuhl, P. K. (1991). Perception, cognition, and the ontogenetic and phylogenetic emergence of human speech. In S. E. Brauth, W. S. Hall, & R. J. Dooling (Eds.), Plasticity of Development (pp. 73–106). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Kuhl, P. K. (1991). [Review of Modularity and the motor theory of speech perception: Proceedings of a conference to honor Alvin M. Liberman, I. G. Mattingly, & M. Studdert-Kennedy, (Eds.)]. Language and Speech, 34, 367–373.
Kuhl, P. K., Williams, K. A., & Meltzoff, A. N. (1991). Cross-modal speech perception in adults and infants using nonspeech auditory stimuli. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 17, 829–840.
Meltzoff, A. N., Kuhl, P. K., & Moore, M. K. (1991). Perception, representation, and the control of action in newborns and young infants: Toward a new synthesis. In M. J. S. Weiss & P. R. Zelazo (Eds.), Newborn Attention: Biological Constraints and the Influence of Experience (pp. 377–411). Norwood, NJ: Ablex.
Kuhl, P. K. (1990). Auditory perception and the ontogeny and phylogeny of human speech. Seminars in Speech and Language, 11, 77–91.
Kuhl, P. K. (1990). Towards a new theory of the development of speech perception. In H. Fujisaki (Ed.), Proceedings of the International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (pp. 745–748). Tokyo, Japan: The Acoustical Society of Japan.
Green, K. P., & Kuhl, P. K. (1989). The role of visual information in the processing of place and manner features in speech perception. Perception & Psychophysics, 45, 34–42.
Grieser, D., & Kuhl, P. K. (1989). Categorization of speech by infants: Support for speech-sound prototypes. Developmental Psychology, 25, 577–588.
Kuhl, P. K. (1989). Infants' acquisition of speech: Evidence of an early understanding of auditory-articulatory correspondences. In J. Erber, R. Menzel, H. Pfluger, & D. Todt (Eds.), Neural Mechanisms of Behavior (pp. 153–154). Stuttgart, Germany: Georg Thieme Verlag.
Kuhl, P. K. (1989). On babies, birds, modules, and mechanisms: A comparative approach to the acquisition of vocal communication. In R. J. Dooling & S. H. Hulse (Eds.), The Comparative Psychology of Audition: Perceiving Complex Sounds (pp. 379–419). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Meltzoff, A. N., & Kuhl, P. K. (1989). Infants’ perception of faces and speech sounds: Challenges to developmental theory. In P. R. Zelazo & R. G. Barr (Eds.), Challenges to Developmental Paradigms: Implications for Theory, Assessment and Treatment (pp. 67–91). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Grieser, D. L., & Kuhl, P. K. (1988). Maternal speech to infants in a tonal language: Support for universal prosodic features in motherese. Developmental Psychology, 24, 14–20.
Kuhl, P. K. (1988). Auditory perception and the evolution of speech. Human Evolution, 3, 19–43.
Kuhl, P. K. (1988). On handedness in primates and human infants. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 11, 727–729.
Kuhl, P. K., & Meltzoff, A. N. (1988). Speech as an intermodal object of perception. In A. Yonas (Ed.), Perceptual Development in Infancy: The Minnesota Symposia on Child Psychology (Vol. 20, pp. 235–266). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Fernald, A., & Kuhl, P. (1987). Acoustic determinants of infant preference for motherese speech. Infant Behavior and Development, 10, 279–293.
Kuhl, P. K. (1987). Perception of speech and sound in early infancy. In P. Salapatek & L. Cohen (Eds.), Handbook of Infant Perception: Vol 2. From Perception to Cognition (pp. 275–382). New York, NY: Academic Press.
Kuhl, P. K. (1987). The special-mechanisms debate in speech research: Categorization tests on animals and infants. In S. Harnad (Ed.), Categorical Perception: The Groundwork of Cognition (pp. 355–386). New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Grant, K. W., Ardell, L. H., Kuhl, P. K., & Sparks, D. W. (1986). The transmission of prosodic information via an electrotactile speechreading aid. Ear and Hearing, 7, 328–335.
Kuhl, P. K. (1986). Infants’ perception of speech: Constraints on characterizations of the initial state. In B. Lindblom & R. Zetterström (Eds.), Precursors of Early Speech (pp. 219–244). New York, NY: Stockton Press.
Kuhl, P. K. (1986). Reflections on infants’ perception and representation of speech. In J. S. Perkell & D. H. Klatt (Eds.), Invariance and Variability in Speech Processes (pp. 19–30). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Kuhl, P. K. (1986). Theoretical contributions of tests on animals to the special-mechanisms debate in speech. Experimental Biology, 45, 233-265.
Grant, K. W., Ardell, L. H., Kuhl, P. K., & Sparks, D. W. (1985). The contribution of fundamental frequency, amplitude envelope, and voicing duration cues to speechreading in normal-hearing subjects. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 77, 671–677.
Kuhl, P. K. (1985). Categorization of speech by infants. In J. Mehler & R. Fox (Eds.), Neonate Cognition: Beyond the Blooming Buzzing Confusion (pp. 231–262). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Kuhl, P. K. (1985). Methods in the study of infant speech perception. In G. Gottlieb & N. Krasnegor (Eds.), Measurement of Audition and Vision in the First Year of Postnatal Life: A Methodological Overview (pp. 223–251). Norwood, NJ: Ablex.
Kuhl, P. K., & Meltzoff, A. N. (1984). The intermodal representation of speech in infants. Infant Behavior & Development, 7, 361–381.
Kuhl, P. K. (1983). Perception of auditory equivalence classes for speech in early infancy. Infant Behavior & Development, 6, 263–285.
Kuhl, P. K. (1983). The perception of speech in early infancy: Four phenomena. In S. E. Gerber & G. T. Mencher (Eds.), The Development of Auditory Behavior (pp. 187–218). New York, NY: Grune & Stratton.
Kuhl, P. K., & Padden, D. M. (1983). Enhanced discriminability at the phonetic boundaries for the place feature in macaques. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 73, 1003–1010.
Kuhl, P. K. (1982). Speech perception: An overview of current issues. In N. J. Lass, L. V. McReynolds, J. L. Northern, & D. E. Yoder (Eds.), Speech, Language, and Hearing: Vol. 1. Normal Processes (pp. 286–322). Philadelphia, PA: Saunders.
Kuhl, P. K., & Meltzoff, A. N. (1982). The bimodal perception of speech in infancy. Science, 218, 1138–1141.
Kuhl, P. K., & Miller, J. D. (1982). Discrimination of auditory target dimensions in the presence or absence of variation in a second dimension by infants. Perception & Psychophysics, 31, 279–292.
Kuhl, P. K., & Padden, D. M. (1982). Enhanced discriminability at the phonetic boundaries for the voicing feature in macaques. Perception & Psychophysics, 32, 542–550.
Kuhl, P. K. (1981). Auditory category formation and developmental speech perception. In R. E. Stark (Ed.), Language behavior in infancy and early childhood (pp. 165–183). New York, NY: Elsevier/North-Holland.
Kuhl, P. K. (1981). Discrimination of speech by nonhuman animals: Basic auditory sensitivities conducive to the perception of speech-sound categories. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 70, 340–349.
Kuhl, P. K. (1980). Infant speech perception: Reviewing data on auditory category formation. In P. Levinson & C. Sloan (Eds.), Auditory Processing and Language: Clinical and Research Perspectives (pp. 35–59). New York, NY: Grune & Stratton.
Kuhl, P. K. (1980). Perceptual constancy for speech-sound categories in early infancy. In G. H. Yeni-Komshian, J. F. Kavanagh & C. A. Ferguson (Eds.), Child Phonology: Vol. 2. Perception (pp. 41–66). New York, NY: Academic Press.
Kuhl, P. K. (1979). Models and mechanisms in speech perception: Species comparisons provide further contributions. Brain, Behavior and Evolution, 16, 374–408.
Kuhl, P. K. (1979). Predispositions for the perception of speech by human infants. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Congress of Phonetic Sciences, Copenhagen, 1979 (pp. 162–168). Copenhagen, Denmark: Institute of Phonetics.
Kuhl, P. K. (1979) Speech perception in early infancy: Perceptual constancy for spectrally dissimilar vowel categories. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 66, 1668–1679.
Kuhl, P. K. (1979). The perception of speech in early infancy. In N. J. Lass (Ed.), Speech and Language: Advances In Basic Research and Practice (pp. 1–47). San Francisco, CA: Academic Press.
Sparks, D. W., Ardell, L. A., Bourgeois, M., Wiedmer, B., & Kuhl, P. K. (1979). Investigating the MESA (Multipoint Electrotactile Speech Aid): The transmission of connected discourse. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 65, 810–815.
Kuhl, P. K. (1978). Predispositions for the perception of speech-sound categories: A species-specific phenomenon? In F. D. Minifie & L. L. Lloyd (Eds.), Communicative and Cognitive Abilities — Early Behavioral Assessment (pp. 229–255). Baltimore, MD: University Park Press.
Kuhl, P. K., & Miller, J. D. (1978). Speech perception by the chinchilla: Identification functions for synthetic VOT stimuli. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 63, 905–917.
Sparks, D. W., Kuhl, P. K., Edmonds, A. E., & Gray, G. P. (1978). Investigating the MESA (Multipoint Electrotactile Speech Aid): The transmission of segmental features of speech. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 63, 246–257.
Kuhl, P. K. (1976). Speech perception in early infancy: The acquisition of speech-sound categories. In S. K. Hirsh, D. H. Eldredge, I. J. Hirsh, & S. R. Silverman (Eds.), Hearing and Davis: Essays Honoring Hallowell Davis (pp. 265–280). St. Louis, MO: Washington University Press.
Kuhl, P. K., & Miller, J. D. (1975). Speech perception by the chinchilla: Voiced-voiceless distinction in alveolar plosive consonants. Science, 190, 69–72.
Ingham, R. J., Martin, R. R., & Kuhl, P. (1974). Modification and control of rate of speaking by stutterers. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research, 17, 489–496.
Martin, R. R., Haroldson, S. K., & Kuhl, P. (1972). Disfluencies of young children in two speaking situations. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research, 15, 831–836.
Martin, R. R., Kuhl, P., & Haroldson, S. (1972). An experimental treatment with two preschool stuttering children. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research, 15, 743–752.
Speaks, C., Parker, B., Harris, C., & Kuhl, P. (1972). Intelligibility of connected discourse. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research, 15, 590–602.
Most Recent Publications
Books and Theoretical Papers
Bilingual Brain
Social Factors in Language Learning
Brain Correlates of Language Processing
Maternal Language Input and Infant Vocal Imitation
Developmental Speech Perception
Autism
Auditory-Visual Speech Perception
Speech Perception: Animal Studies
Mittag, M., Larson, E., Clarke, M., Taulu, S., & Kuhl, P. K. (2021). Auditory deficits in infants at risk for dyslexia during a linguistic sensitive period predict future language. NeuroImage, 30, 102578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2021.102578
Kuhl, P. K. (2021, in press). Language. In E. R. Kandel, J. D. Koester, S. H. Mack, & S. A. Siegelbaum (Eds.), Principles of neural science (6th ed.). McGraw Hill.
Kuhl, P. K. (2021, in press). Infant speech perception: Integration of multimodal data leads to a new hypothesis—Sensorimotor mechanisms underlie learning. In Minnesota Symposia on Child Psychology (Vol. 40, pp. 113–158). Wiley.
Ferjan Ramírez, N., Hippe, D. S., & Kuhl, P. K. (2021). Comparing automatic and manual measures of parent-infant conversational turns: A word of caution. Child Development.
https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.13495
Corrigan, N. M., Varnykh, V. L., Hippe, D. S., Owen, J. P., Huber, E., Zhoa, T. C., & Kuhl, P. K. (2021). Myelin development in cerebral gray and white matter during adolescence and late childhood. NeuroImage, 277, 117678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117678
Bosseler, A. N., Clarke, M., Tavabi, K., Larson, E. D., Hippe, D. S., Taulu, S., & Kuhl, P. K. (2021). Using magnetoencephalography to examine word recognition, lateralization, and future language skills in 14-month-old infants. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 47, 100901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2020.100901
Sundara, M., Wards, N., Conboy, B., & Kuhl, P. K. (2020, in press). Exposure to a second language in infancy alters speech production. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition. Click here to receive a reprint
Mamiya, P. C., Richards, T., Corrigan, N. M., & Kuhl, P. K. (2020). Strength of ventral tegmental area connections with left caudate nucleus is related to conflict monitoring. Frontiers in Psychology. On-line access prior to publication, doi.org/10.33.89/fpsyg.2019.02869 Click here to receive a reprint
Ferjan Ramírez, N., Lytle, S., & Kuhl, P. K. (2020, in press). Parent coaching increases conversational turns and advances infant language development. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Click here to receive a reprint
Ferjan Ramírez, N., & Kuhl, P. K. (2020). Early second language learning through SparkLing™: Scaling up a language intervention in infant education centers. Mind, Brain, and Education. On-line access prior to publication, doi.org/10.1111/mbe.12232 Click here to receive a reprint
Zhao, M., Masapollo, M., Polka, L., Menard, L. & Kuhl, P. K. (2019). Effects of formant proximity and stimulus prototypicality on the neural discrimination of vowels: Evidence from the auditory Frequency-Following Response. Brain and Language, 194, 77–83. Click here to receive a reprint
Lin, J.-F. L., Imada, T., & Kuhl, P. K. (2019). Neuroplasticity, bilingualism, and mental mathematics: A behavior-MEG study. Brain and Cognition, 134, 122–134. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K., Lim, S.-S., Guerriero, S. & Van Damme, D. (2019). Developing Minds in the Digital Age: Towards a Science of Learning for 21st Century Education. Paris, France: OECD Publishing. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K., & Ferjan Ramírez, N. (2019). Neuroscience and education: How early brain development affects school. In P. K. Kuhl, S.-S. Lim, S. Guerriero & D. Van Damme (Eds.), Developing Minds in the Digital Age: Towards a Science of Learning for 21st Century Education. Paris, France: OECD Publishing. Click here to receive a reprint
Zhao, T. C., & Kuhl, P. K. (2018). Linguistic effect on speech perception observed at the brainstem. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 115, 8716–8721. Click here to receive a reprint
Mamiya, P. C., Richards, T. L., & Kuhl, P. K. (2018). Right forceps minor and anterior thalamic radiation predict executive function skills in young bilingual adults. Frontiers in Psychology-Language Sciences, 9, 1–10. Click here to receive a reprint
Lytle, S. R., & Kuhl, P. K. (2018). Social interaction and language acquisition: Toward a neurobiological view. In E. M. Fernández & H. S. Cairns (Eds.), Blackwell Handbooks in Linguistics. The Handbook of Psycholinguistics (pp. 615–634). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Blackwell. Click here to receive a reprint
Lytle, S. R., García-Sierra, A., & Kuhl, P. K. (2018). Two are better than one: Infant language learning from video improves in the presence of peers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115, 9859–9866. Click here to receive a reprint
Lin, J.-F. L., Imada., Kuhl, P. K., & Lin, F.-H. (2018). Incongruent pitch cues are associated with increased activation and functional connectivity in the frontal areas. Scientific Reports, 8, 5206. DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-23287-5 Click here to receive a reprint
Ferjan Ramírez, N., Ramírez, R. R., Clarke, M., Taulu, S., & Kuhl, P. K. (2017). Speech discrimination in 11‐month‐old bilingual and monolingual infants: a magnetoencephalography study. Developmental Science, 20(1), e12427. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K. & Damasio, A. (2012). Language, in E. R. Kandel. J. H. Schwartz, T. M. Jessell, S. Siegelbaum, & J. Hudspeth (Eds.), Principles of neural science: 5th Edition (pp. 1353-1372). New York: McGraw Hill. Click here to receive a reprint
Ramirez-Esparza, N., Harris, K., Hellermann, J., Clemence, R., Kuhl, P. K., & Reder, S. (2012). Socio-interactive practices and personality in adult learners of English with little formal education. Language Learning, 62, 541-570. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K. (2011). Who's Talking? Science, 333, 529-530. Click here to receive a reprint | Perspective on Perrachione
Kuhl, P. K. (2011). Early language learning and literacy: Neuroscience implications for education. Mind, Brain, and Education, 5, 128-142. Click here to receive a reprint
Sundara, M., Demuth, K. & Kuhl, P. K. (2011). Sentence-position effects on children’s perception and production of English 3rd person singular –s. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 54, 55-71. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P.K. (2010). Brain Mechanisms in Early Language Acquisition. Neuron, 67, 713-727. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K. (2009). Early language acquisition: Neural substrates and theoretical models. In M. S. Gazzaniga (Ed.), The Cognitive Neurosciences, 4th Edition (pp. 837-854). Cambridge, MA.: MIT Press. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K. (2009). Early language acquisition: Phonetic and word learning, neural substrates, and a theoretical model. In B. Moore, L. Tyler & W. Marslen-Wilson (Eds.), The Perception of Speech: From Sound to Meaning (pp 103-131). Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. Click here to receive a reprint
Meltzoff, A. N., Kuhl, P. K., Movellan, J., & Sejnowski, T. J. (2009). Foundations for a New Science of Learning. Science, 325, 284-288. Click here to receive a reprint
Conboy, B.T., Sommerville, J., & Kuhl, P. K. (2008). Cognitive control factors in speech perception at 11 months. Developmental Psychology, 44, 1505-1512. Click here to receive a reprint
Doupe, A. J. & Kuhl, P. K. (2008). Birdsong and human speech: Common themes and mechanisms. In H. P. Zeigler, & P. Marler (Eds.), Neuroscience of Birdsong (pp. 5-31). Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K. (2008). Linking infant speech perception to language acquisition: Phonetic learning predicts language growth. In P. McCardle, J. Colombo & L. Freund (Eds.), Infant pathways to language: Methods, models, and research directions (pp. 213-244). New York: Erlbaum. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K., Conboy, B. T., Coffey-Corina, S., Padden, D., Rivera-Gaxiola, M. & Nelson, T. (2008). Phonetic learning as a pathway to language: new data and native language magnet theory expanded ( NLM-e). Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 363, 979-1000. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K. & Rivera-Gaxiola, M. (2008). Neural substrates of language acquisition. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 31, 511-534. Click here to receive a reprint
Raizada, R. D., Richards, T. L., Meltzoff, A. M. & Kuhl, P. K. (2008). Socioeconomic status predicts hemispheric specialization of the left inferior frontal gyrus in young children. NeuroImage, 40, 1392-1401. Click here to receive a reprint
Bransford, J., Vye, N., Stevens, R., Kuhl, P. K., Schwartz, D., Bell, P., Meltzoff, A., Barron, B., Pea, R., Reeves, B., Roschelle, J., & Sabelli, N. (2006). Learning theories and education: Toward a decade of synergy. In P. Alexander & P. Winne (Eds.), Handbook of Educational Psychology, 2nd edition (pp. 209-244). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum. Click here to receive a reprint
Bransford, J. D., Barron, B., Pea, R., Meltzoff, A. N., Kuhl, P. K., Bell, P., Stevens, R., Schwartz, D., Vye, N., Reeves, B., Roschelle, J. & Sabelli, N. (2006). Foundations and opportunities for an interdisciplinary science of learning. In K. Sawyer (Ed.), The Cambridge Handbook of the Learning Sciences (pp. 39-77). New York: Cambridge University Press. Click here to receive a reprint
Liu, H-M., Tsao, F-M., and Kuhl, P. K. (2005). The effect of reduced vowel working space on speech intelligibility in Mandarin-speaking young adults with cerebral palsy. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 117, 3879-3889. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K. (2004). Early language acquisition: Cracking the speech code. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 5, 831-843. Click here to receive a reprint
Iverson, P., Kuhl, P. K., Akahane-Yamada, R., Diesch, E., Tohkura, Y., Kettermann, A., & Siebert, C. (2003). A perceptual interference account of acquisition difficulties for non-native phonemes. Cognition, 87, B47-B57. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K., Tsao, F. -M., Liu, H. -M., Zhang, Y., & de Boer, B. (2001). Language/Culture/Mind/Brain: Progress at the margins between disciplines. In A. Domasio et al. (Eds.). Unity of knowledge: The convergence of natural and human science (pp. 136-174). New York: The New York Academy of Sciences. Click here to receive a reprint
 Gopnik, A., Meltzoff, A. N., & Kuhl, P. K. (2000). The scientist in the crib: What early learning tells us about the mind. New York: HarperCollins. (Read an excerpt.)
Gopnik, A., Meltzoff, A. N., & Kuhl, P. K. (2000). The scientist in the crib: What early learning tells us about the mind. New York: HarperCollins. (Read an excerpt.)
Kuhl, P. K. (2000). A new view of language acquisition. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, 97, 11850-11857. Click here to receive a reprint
Iverson, P., & Kuhl, P. K. (2000). Perceptual magnet and phoneme boundary effects in speech perception: Do they arise from a common mechanism? Perception and Psychophysics, 62, 874-886. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K. (2000). Language, mind, and brain: Experience alters perception. In M. S. Gazzaniga (Ed.), The new cognitive neurosciences (2nd ed.) (pp. 99-115). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. Click here to receive a reprint
Doupe, A., & Kuhl, P. K. (1999). Birdsong and speech: Common themes and mechanisms. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 22, 567-631. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K. (1998). The development of speech and language. In T. J. Carew, R. Menzel, & C. J. Shatz (Eds.), Mechanistic relationships between development and learning (pp. 53-73). New York: Wiley. Click here to receive a reprint
Iverson, P., & Kuhl, P. K. (1996). Influences of phonetic identification and category goodness on American listeners' perception of /r/ and /l/. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 99, 1130-1140. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K. (1994). Learning and representation in speech and language. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 4, 812-822. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K. (1993). Innate predispositions and the effects of experience in speech perception: The native language magnet theory. In B. deBoysson-Bardies, S. de Schonen, P. Jusczyk, P. McNeilage, & J. Morton (Eds.), Developmental neurocognition: Speech and face processing in the first year of life (pp. 259-274). Dordrecht, Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers. Click here to receive a reprint
Lin, J.-F. L., Imada, T., & Kuhl, P. K. (2012). Mental addition in bilinguals: An fMRI study of task-related and performance-related activation. Cerebral Cortex, doi:10.1093/cercor/bhr263. Click here to receive a reprint
Garcia-Sierra, A., Rivera-Gaxiola, M., Conboy, B. T., Romo, H., Percaccio, C. R., Klarman, L., Ortiz, S., & Kuhl, P. K. (2011). Socio-cultural environment and bilingual language learning: A longitudinal event related potential study. Journal of Phonetics, 39, 456-557. Click here to receive a reprint
Wang, Y., Kuhl, P. K., Chen, C., & Dong, Q. (2009). Sustained and transient language control in the bilingual brain. NeuroImage, 47, 414-422. Click here to receive a reprint
Wang, Y., Lin, J.-F., Kuhl, P. K., Hirsch, J. (2007). Mathematical and linguistic processing differs between native and second languages: An fMRI study. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 1, 68-82. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K. (2011). Social mechanisms in early language acquisition: Understanding integrated brain systems supporting language. In J. Decety & J. Cacioppo (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of social neuroscience (pp. 649-667). Oxford UK: Oxford University Press. Click here to receive a reprint
Conboy, B. T. & Kuhl, P. K. (2011). Impact of second-language experience in infancy: Brain measures of first- and second-language speech perception. Developmental Science, 14, 242-248. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K. (2007). Is speech learning 'gated' by the social brain? Developmental Science, 10, 110-120. Click here to receive a reprint
Conboy, B. & Kuhl, P. K. (2007). Listening to language in culturally specific ways: Learning through social experience. In S. Braten (Ed.), Foundations of Preverbal Intersubjectivity: Being Moved by Action-Perception, Music and Speech. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, England. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K., Tsao. F.-M., & Liu, H.-M. (2003). Foreign-language experience in infancy: Effects of short-term exposure and social interaction on phonetic learning. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 100, 9096-9101. Click here to receive a reprint
Can, D. C., Richards, T. L., & Kuhl, P. K. (2013). Early gray-matter and white-matter concentration in infancy predict later language skills: A whole-brain voxel-based morphometry study. Brain & Language, 124, 34-44. Click here to receive a reprint
Lin, J.-F. L., Imada, T., & Kuhl, P. K. (2012). Mental addition in bilinguals: an fMRI study of task-related and performance-related activation. Cerebral Cortex, doi:10.1093/cercor/bhr263. Click here to receive a reprint
Rivera-Gaxiola. M., Garcia-Sierra, A., Lara-Ayala, L., Cadena, C., Jackson-Maldonado, D., & Kuhl, P. K. (2012). Event-related potentials to an English/Spanish syllabic contrast in Mexican 10-13 month-old infants. ISRN Neurology, doi:10.5402/2012/702986. Click here to receive a reprint
Raizada, R. D., Tsao, F. M., Liu, H. M., Holloway, I. D., Ansari, D., & Kuhl, P. K. (2010). Linking brain-wide multivoxel activation patterns to behaviour: Examples from language and math. NeuroImage, 51, 462-471. Click here to receive a reprint
Raizada, R. D. S., Tsao, F. M., Liu, H. M., & Kuhl, P. K. (2010). Quantifying the adequacy of neural representations for a cross-language phonetic discrimination task: Prediction of individual differences. Cerebral Cortex, 20, 1-12. Click here to receive a reprint
Zhang, Y., Kuhl, P. K., Imada, T., Iverson, P., Pruitt, J., Stevens, E. B., Kawakatsu, M., Tohkura, Y., & Nemoto, I. (2009). Neural signatures of phonetic learning in adulthood: A magnetoencephalography study. NeuroImage, 46, 226-240. Click here to receive a reprint
Conboy, B. T., Rivera-Gaxiola, M., Silva-Pereyra, J., & Kuhl, P. K. (2008). Event-related potential studies of early language processing at the phoneme, word, and sentence levels. In A. D. Friederici & G. Thierry (Eds.), Trends in Language Acquisition Research, 5, 23-64. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K. & Rivera-Gaxiola, M. (2008). Neural substrates of language acquisition. Anuual Review of Neuroscience. 31, 511-534. Click here to receive a reprint
Rivera-Gaxiola, M., Silva-Pereyra, J., Klarman, L., Garcia-Sierra, A., Lara-Ayala, L., Cadena-Salazar, C. & Kuhl, P. K. (2007). Principal component analyses and scalp distribution of the auditory P150-250 and N250-550 to speech contrasts in Mexican and American infants. Developmental Neuropsychology, 31, 363-378. Click here to receive a reprint
Silva-Pereyra, J., Conboy, B.T., Klarman, L., & Kuhl, P. K. (2007). Grammatical processing without semantics? An event-related brain potential study of preschoolers using jabberwocky sentences. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 19, 1050-1065. Click here to receive a reprint
Imada, T., Zhang, Y., Cheour, M., Taulu, S., Ahonen, A. & Kuhl, P. K. (2006). Infant speech perception activates Broca's area: a developmental magnetoencephalography study. NeuroReport, 17, 957-962. Click here to receive a reprint
Zhang, Y., Kuhl, P. K., Imada, T., Kotani, M., & Tohkura, Y. (2005). Effects of language experience: Neural commitment to language-specific auditory patterns. NeuroImage. 26, 703-720. Click here to receive a reprint
Rivera-Gaxiola, M., Klarman, L., Garcia-Sierra, A. & Kuhl, P. K. (2005). Neural patterns to speech and vocabulary growth in American infants. NeuroReport, 16, 495-498. Click here to receive a reprint
Silva-Pereyra, J., Klarman, L., Lin, J. F. & Kuhl, P. K. (2005). Sentence processing in 30-month old children: An ERP study. NeuroReport, 16, 645-648. Click here to receive a reprint
Rivera-Gaxiola, M., Silva-Pereyra, J. & Kuhl, P. K. (2005). Brain potentials to native and non-native speech contrasts in 7- and 11-month-old American infants. Developmental Science, 8, 162-172. Click here to receive a reprint
Silva-Pereyra, J., Rivera-Gaxiola, M. & Kuhl, P. K. (2005). An event-related brain potential study of sentence comprehension in preschoolers: Semantic and morphosyntactic processing. Cognitive Brain Research, 23, 247-258. Click here to receive a reprint
Moon, C., Lagercrantz, H., & Kuhl, P. K. (2012). Language experienced in utero affects vowel perception after birth: a two-country study, Acta Pediatrica, 102, 156-160. Click here to receive a reprint
Zhao, T. C., Moon, C., Lagercrantz, H., & Kuhl, P. K. (2011). Prenatal motherese? Newborn speech perception may be enhanced by having a young sibling. Psi Chi Journal of Undergraduate Research, 16, 90-94. Click here to receive a reprint
Liu, H. M., Tsao, F. M., & Kuhl, P. K. (2009). Age-related changes in acoustic modifications of Mandarin maternal speech to preverbal infants and five-year-old children: A longitudinal study. Journal of Child Language, 36, 909-922. Click here to receive a reprint
Liu, H. M., Tsao, F. M., & Kuhl, P. K. (2007). Acoustic analysis of lexical tone in Mandarin infant-directed speech. Developmental Psychology, 43, 912-917. Click here to receive a reprint
Liu, H. M., Kuhl, P. K., & Tsao, F. M. (2003). An association between mothers' speech clarity and infants' speech discrimination skills. Developmental Science, 6, F1-F10. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K., Tsao, F. M., Liu, H. M., Zhang, Y., & de Boer, B. (2001). Language/Culture/Mind/Brain: Progress at the margins between disciplines. In A. Domasio et al. (Eds.). Unity of knowledge: The convergence of natural and human science (pp. 136-174). New York: The New York Academy of Sciences. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K., Andruski, J. E., Chistovich, I. A., Chistovich, L. A., Kozhevnikova, E. V., Ryskina, V. L., Stolyarova, E. I., Sundberg, U., and Lacerda, F. (1997). Cross-language analysis of phonetic units in language addressed to infants. Science, 277, 684-686. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K., & Meltzoff, A. N. (1996). Infant vocalizations in response to speech: Vocal imitation and developmental change. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 100, 2425-2438. Click here to receive a reprint
Grieser, D. L., & Kuhl, P. K. (1988). Maternal speech to infants in a tonal language: Support for universal prosodic features in motherese. Developmental Psychology, 24, 14-20. Click here to receive a reprint
Fernald, A., & Kuhl, P. K. (1987). Acoustic determinants of infant preference for motherese speech. Infant Behavior and Development, 10, 279-293. Click here to receive a reprint
Lebedeva, G. C., & Kuhl, P. K. (2010). Sing that tune: Infants' perception of melody and lyrics and the facilitation of phonetic recognition in songs. Infant Behavior and Development, 33, 419-430. Click here to receive a reprint
Tsao, F.-M., Liu, H.-M., Kuhl, P. K. (2006). Perception of native and non-native affricate-fricative contrasts: Cross-language tests on adults and infants. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 120, 2285-2294. Click here to receive a reprint
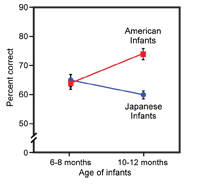
Kuhl, P. K., Stevens, E., Hayashi, A., Deguchi, T., Kiritani, S. & Iverson, P. (2006). Infants show a facilitation effect for native language phonetic perception between 6 and 12 months. Developmental Science, 9, F13-F21. Click here to receive a reprint
Conboy, B., Rivera-Gaxiola, M., Klarman, L., Aksoylu, E. & Kuhl, P.K. (2005). Associations between native and nonnative speech sound discrimination and language development at the end of the first year. Proceedings Supplement of the 29th Annual Boston University Conference on Language Development (pp. 1-11). Click here to receive a reprint
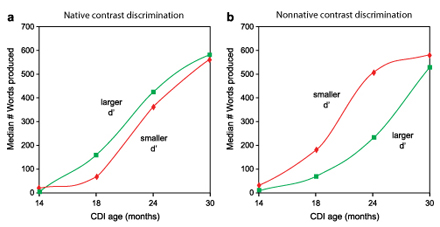
Kuhl, P. K., Conboy, B. T., Padden, D., Nelson, T. & Pruitt, J. (2005). Early speech perception and later language development: Implications for the "critical period." Language Learning and Development, 1, 237-264. Click here to receive a reprint
Tsao, F.-M., Liu, H.-M., & Kuhl, P. K. (2004). Speech perception in infancy predicts language development in the second year of life: A longitudinal study. Child Development, 75, 1067-1084. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K., Williams, K. A., Lacerda, F., Stevens, K. N., & Lindblom, B. (1992). Linguistic experience alters phonetic perception in infants by 6 months of age. Science, 255, 606-608. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K. (1991). Human adults and human infants show a "perceptual magnet effect" for the prototypes of speech categories, monkeys do not. Perception & Psychophysics, 50, 93-107. Click here to receive a reprint
Grieser, D., & Kuhl, P. K. (1989). Categorization of speech by infants: Support for speech-sound prototypes. Developmental Psychology, 25, 577-588. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K., Coffey-Corina, S., Padden, D., Munson, J., Estes, A., & Dawson, G. (2013). Brain responses to words in 2-year-olds with autism predict developmental outcomes at age 6. PLOS ONE, 8, e64967. Click here to receive a reprint
Coffey-Corina, S., Padden, D., Kuhl, P. K. & Dawson, G. (2008). ERPs to words correlate with behavioral measures in children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 123, 3742. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K., Coffey-Corina, S., Padden, D., & Dawson, G. (2005). Links between social and linguistic processing of speech in preschool children with autism: Behavioral and electrophysiological measures. Developmental Science, 8, F1-F12. Click here to receive a reprint
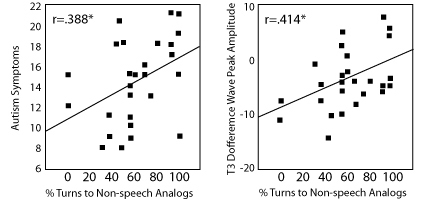
Kuhl, P. K., & Meltzoff, A. N. (1997). Evolution, nativism, and learning in the development of language and speech. In M. Gopnik (Ed.), The inheritance and innateness of grammars (pp. 7-44). New York: Oxford University Press. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K., Tsuzaki, M., Tohkura, Y., & Meltzoff, A. N. (1994). Human processing of auditory-visual information in speech perception: Potential for multimodal human-machine interfaces. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (pp. 539-542). Tokyo: Acoustical Society of Japan. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K., Williams, K. A., & Meltzoff, A. N. (1991). Cross-modal speech perception in adults and infants using nonspeech auditory stimuli. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 17, 829-840. Click here to receive a reprint
Green, K. P., Kuhl, P. K., Meltzoff, A. N., & Stevens, E. B. (1991). Integrating speech information across talkers, gender, and sensory modality: Female faces and male voices in the McGurk effect. Perception & Psychophysics, 50, 524-536. Click here to receive a reprint
Green, K. P., & Kuhl, P. K. (1991). Integral processing of visual place and auditory voicing information during phonetic perception. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 17, 278-288. Click here to receive a reprint
Green, K. P., & Kuhl, P. K. (1989). The role of visual information in the processing of place and manner features in speech perception. Perception & Psychophysics, 45, 34-42. Click here to receive a reprint
Meltzoff, A. N., & Kuhl, P. K. (1989). Infants' perception of faces and speech sounds: Challenges to developmental theory. In P. R. Zelazo & R. G. Barr (Eds.), Challenges to developmental paradigms: Implications for theory, assessment and treatment (pp. 67-91). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K., & Meltzoff, A. N. (1982). The bimodal perception of speech in infancy. Science, 218, 1138-1141. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K. (1999). Speech, language, and the brain: Innate preparation for learning. In M. Konishi & M. Hauser (Eds.), Neural mechanisms of communication (pp. 419-450). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K. (1991). Perception, cognition, and the ontogenetic and phylogenetic emergence of human speech. In S. E. Brauth, W. S. Hall, & R. J. Dooling (Eds.), Plasticity of development (pp. 73-106). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K. (1989). On babies, birds, modules, and mechanisms: A comparative approach to the acquisition of vocal communication. In R. J. Dooling & S. H. Hulse (Eds.), The comparative psychology of audition: Perceiving complex sounds (pp. 379-419). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K. (1988). Auditory perception and the evolution of speech. Human Evolution, 3, 19-43. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K., & Padden, D. M. (1983). Enhanced discriminability at the phonetic boundaries for the place feature in macaques. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 73, 1003-1010. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K., & Padden, D. M. (1982). Enhanced discriminability at the phonetic boundaries for the voicing feature in macaques. Perception & Psychophysics, 32, 542-550. Click here to receive a reprint
Kuhl, P. K., & Miller, J. D. (1975). Speech perception by the chinchilla: Voiced-voiceless distinction in alveolar plosive consonants. Science, 190, 69-72. Click here to receive a reprint

Dr. Kuhl's Speech Research Lab is part of the UW Institute for Learning and Brain Sciences, of which she is co-director. Her lab is on the university's Seattle campus. Below are details about the researchers, postdoctoral fellows, and research staff members who work with Dr. Kuhl at the Institute, as well as information about her colleagues at other institutions and her former lab members.
Alexis Bosseler, Ph.D.
Dr. Alexis Bosseler is a research scientist at the Institute of Learning and Brain Sciences and research fellow at the Cognitive Brain Research Unit at the University of Helsinki. She received her BA in developmental psychology at the University of California Santa Cruz and her Ph.D. in Speech and Hearing Sciences at the University of Washington. Her research, which utilizes behavioral measures and neurophysiological methods (event-related potentials/electroencephalography and magnetoencephalography), focuses on the development of language and cognitive processing in infants and children. Alexis has also conducted research on the speech processing skills of children with autism with Dominic Massaro in the Perceptual Science Laboratory at UC Santa Cruz.
Naja Ferjan Ramirez, Ph.D.
Naja Ferjan Ramirez, Ph. D., is a Research Scientist working in Dr. Patricia Kuhl's lab. Naja earned her Bachelor's degree in Neuroscience from Brown University and her Ph.D. in Linguistics and Cognitive Science from the University of California, San Diego. Her research broadly focuses on understanding the brain-based mechanisms of language acquisition in populations from various linguistic backgrounds. Currently, Naja is conducting brain (magnetoencephalography) and behavioral studies with babies who are simultaneously acquiring two languages (bilinguals). Naja is also a mother of two young children who are learning three languages (Slovene, Spanish, and English).
Ping Mamiya, Ph.D.
Dr. Mamiya is a research scientist working with Dr. Patricia Kuhl on how dopamine and serotonin mediates language learning through modulation of neural activity in the prefrontal cortex. She earned her Ph.D. in Department of Biopsychology and Behavioral Neuroscience at Rutgers University where she investigated the dysfunctions of dopamine and serotonin systems in EphA5 knockout animal, and developed a nanofiber system to enhance the growth of dopaminergic neurons. Her research at I-LABS focuses on the relationship between the language learning ability and 1) polymorphism of dopamine and serotonin transporter genes and 2) the size of dopamine and serotonin projection fibers to the prefrontal cortex. By examining these relationships in both adults and infants, her research aims to further our understanding of how social interactions may facilitate language learning through dopamine/serotonin mediated modulation of prefrontal executive functions.
Maria Mittag, Ph.D.
Maria is a post-doctoral fellow working in Dr. Patricia Kuhl’s lab. Maria obtained her Master’s degree in Psychology from the Technical University of Dresden, Germany. She received her PhD from the Cognitive Brain Research Unit, Finland, working with Professor Teija Kujala, Professor Kimmo Alho, and Professor Risto Näätänen. Her PhD work resulted in four peer-reviewed international publications on audiovisual processing in fluent readers and readers with dyslexia. At I-LABS, Maria investigates early brain markers of dyslexia by using EEG, MEG, MRI, and behavioral testing. In her free time, she enjoys travel and hiking.
Kambiz Tavabi, Ph.D.
Dr. Tavabi is a research scientist working with Dr. Patricia Kuhl on studies of speech and language neuroscience in infants. He earned a Ph.D. in cognitive psychology at the Institute for Biomagnetism and Biosignal Analysis in Muesnter Germany with Dr. Christo Pantev. Dr. Tavabi's research interests focus on the neurobiological basis of speech and auditory language. His research employs magnetoencephalography (MEG) to measure brain activity involved in phonological and/or semantic processing. Before coming to the Institute, Dr. Tavabi was a post-doctoral fellow at the Children's Hospital in Philadelphia where he used MEG to study abnormal brain function during spoken word recognition in children with Autism. In his current work, he is looking at cortical networks underlying spoken word recognition in typically developing infants in order to develop diagnostic measures of the various language impairments encountered by children suffering from autism. Dr. Tavabi's tenure at I-LABS is funded by a generous donation awarded through the Bezo's Family Foundation.
Christina Zhao, Ph.D.
Christina (Tian) Zhao is a posdoctoral fellow in Dr. Patricia Kuhl's lab. She graduated from Pacific Lutheran University in Tacoma, Washington with a Bachelor's degree in Psychology, with minors in Biology and Music. The research questions that interest her most are concerning the interaction between music and speech perception and how experience in a particular sound environment shapes one's perception of sounds.
Melanie Fish
Ms. Fish graduated from the University of Washington in 2011, with a bachelor’s degree in Linguistics and a minor in Italian. As a research assistant in Dr. Patricia K. Kuhl’s lab, Melanie is currently aiding in investigations of the perception/discrimination of speech sounds by monolingual and bilingual adults and infants, using event-related potential (ERP) technology. In Fall 2013, Melanie will pursue a doctorate in Speech and Hearing Sciences. Her primary areas of interest include cognitive science, neurolinguistics, and first language acquisition.
Neva Corrigan, Ph.D.
Neva Corrigan is a research scientist in Dr. Patricia Kuhl’s laboratory. Neva earned a BS from Cornell University, and a MS and PhD in Biomedical Engineering from the University of California at Davis, with a focus on medical imaging. Her PhD studies focused on MRI data acquisition and analysis, with a dissertation on the development of a digital filtering algorithm for the removal of physiological noise from fMRI images. Over the past 14 years, she has utilized her extensive signal and image processing expertise in the analysis and interpretation of MRI and electrophysiological data with investigators at the UW in the Departments of Radiology and Neurological Surgery, as well as the UW Autism Center. Neva has worked extensively with Dr. Stephen Dager in the Department of Radiology, using innovative 2D and 3D magnetic resonance spectroscopic (MRS) imaging techniques to study brain chemical alterations associated with autism spectrum disorder in infants and children. Her interests in Dr. Kuhl’s lab include co-registration of electrophysiological and MRI/MRS data, as well as innovative techniques for quantitative assessment of brain structural changes associated with early childhood development.
Julia Mizrahi
Ms. Mizrahi supports studies of speech processing in infants and young children using a variety of methods including brain imaging technology. She recruits and schedules families for various research studies, as well as assisting the Speech Research Laboratory faculty and staff in their ongoing projects related to MEG, MRI, and ERP. She has experience working with diverse populations including infants and children residing in the United States and abroad. Ms. Mizrahi received her bachelors degree in Peace Studies with minors in Political Science and Art from Goucher College in 2011.
Jean Andruski, Ph.D., Interim Chair, Department of Communitcation Sciences and Disorders, Wayne State University, Detroit, Michigan
Bart de Boer, Ph.D., NWO-vidi researcher, University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Adrian Garcia-Sierra, Ph.D., Assistant Professor, Department of Speech, Language, and Hearing Sciences, University Connecticut, Storrs, Connecticut
Michael Hall, Ph.D., Professor, Director of Psychology Science Programs, Department of Psycology, James Madison University, Harrisonburg, Virginia
Paul Iverson, Ph.D., Reader in Speach Sciences, Department of Phonetics and Linguistics, University College London, London, England
Huei-Mei Liu, Ph.D., Assistant Professor, Department of Special Education, National Taiwan Normal University, Taipei, Taiwan
Sarah Roseberry Lytle, Ph.D., Director of Outreach and Education, I-LABS, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington
Rajeev Raizada, Ph.D. Research Assistant Professor, Neukom Institute for Computational Science, Dartmouth College, Hanover, New Hampshire
Nairan Ramirez-Esparza, Ph.D., Assistant Professor of Psychology, University of Connecticut, Storrs, Connecticut
Sandra Serafini, Assistant Professor, Department of Surgery-Neurosurgery, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina
Cherie Percaccio, Ph.D., No current affiliation
Juan Silva-Pereyra, Assistant Professor, Cognitive Neuroscience & Psycholinguistics, University of La Laguna, Tenerife, Spain
Megha Sundara, Ph.D., Assistant Professor, Department of Linguistics, University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, California
Chiara Suttora, Research Fellow, Department of Psychology, University of Milano-Bicocca, Milan, Italy.
Feng-Ming Tsao, Ph.D., Assistant Professor, Department of Early Childhood Education, National Taipei Teachers College, Taipei, Taiwan
Yapeng Wang, Ph.D., Associate Professor, National Key Laboratory of Cognitive Neuroscience and Learning, Beijing, Normal University, China
Yue Wang, Ph.D., Lab Director, Associate Professor, Linquistics, Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, British Columbia
Yang Zhang, Assistant Professor, Department of Speech-Language-Hearing Sciences, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota